Whether you are a professional woodworker, setting up a warehouse, or running a construction company, saws are indispensable tools for achieving precise and efficient cuts in various materials. Both manual and power saws allow operators to efficiently trim and cut through wood, stone, ceramic, metal, and plastic. There are many types of saws with specific applications ranging from removing trees to tiling a bathroom, so be sure to choose the best tool for the project ahead.
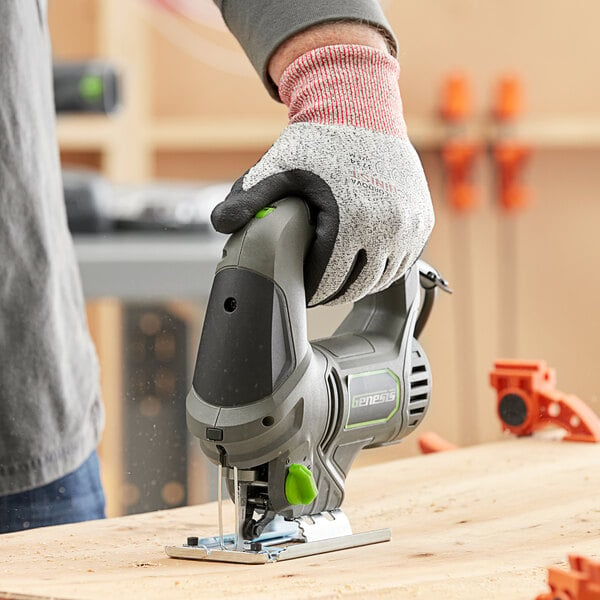

1. Jigsaw
A jigsaw is a versatile power saw that makes intricate curved cuts in various materials, such as wood, metal, plastic, and laminate. It has a thin, narrow blade that moves in a rapid up-and-down motion, allowing for precise and controlled cuts. Jigsaw blades come in different shapes and sizes, each achieving a distinct cut ranging from straight lines to spirals. After marking out a guide on the material, position the jigsaw’s shoe firmly on the marked cut line and apply gentle, steady pressure to ensure a smooth and accurate cut.
- Type: Handheld power saw
- Best for: Versatility, curved or irregular cuts
- Average size: 7″ blade
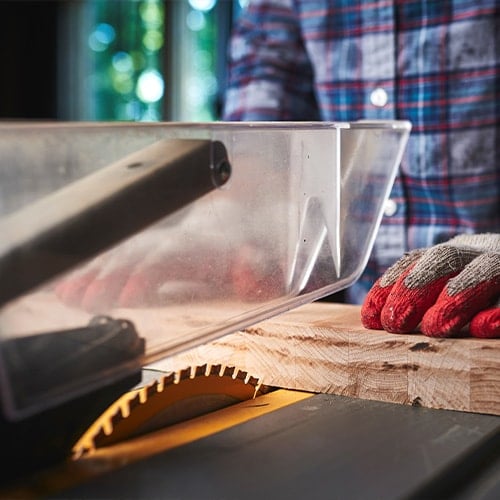

2. Table Saw
With its flat table-like surface and a circular saw blade protruding from the center, a table saw provides stability and accuracy for making straight cuts. Since the blade is stationary at the center of the tabletop, operators have a stable surface for materials as they work. Adjust the carbide-tipped blade to alter the cutting depths and cut type, then hold the material against the fence and gently push it into the rotating blade using a push stick or block.
- Type: Stationary power saw
- Best for: Precise cuts of large pieces of wood
- Average size: 10″ blade diameter
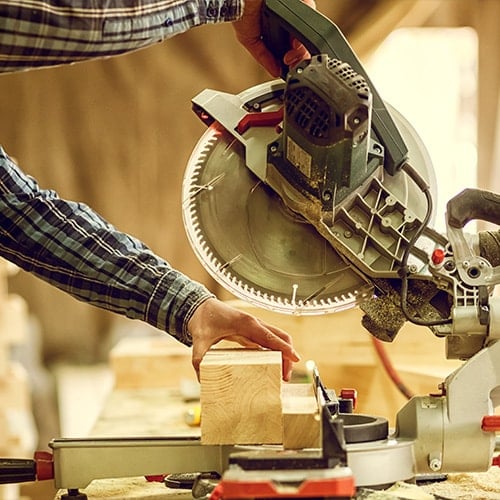

3. Miter Saw
A miter saw stands apart by making angled cuts, also known as miters, in wood and other soft materials. This ability is crucial for making miter joints where two pieces of wood join seamlessly at an angle. A miter saw typically consists of a circular blade mounted on a hinged arm connected to a base, which you can situate on a workbench or tabletop. The base includes a rotating table that allows the user to adjust the angle of the cut.
For more flexibility, consider a compound miter saw. It features a pivot lever to provide more cutting options.
- Type: Power saw
- Best for: Precise, angled cuts
- Average size: 8″, 10″, and 12″ blade diameters
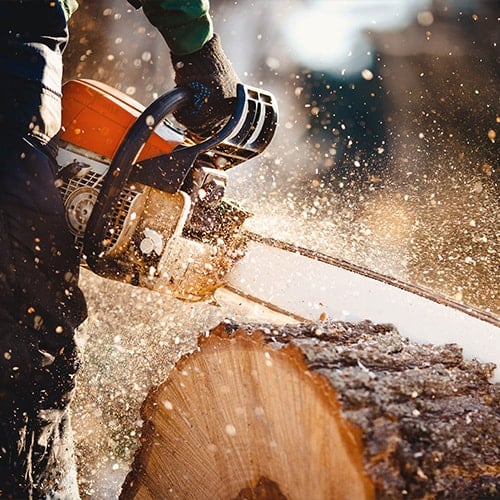

4. Chainsaw
Commonly used in forestry and construction, a chainsaw is a perfect option for trimming trees and bushes or felling trees altogether. It consists of a guidebar extending from the saw’s body, a chain with sharp teeth wrapped around the guidebar, and an engine powered by gas or electricity. Some electric chainsaws use a battery to eliminate long power cords, allowing operators to move between areas easily.
- Type: Portable power saw
- Best for: Cutting lumber, trimming shrubbery, and felling trees
- Average size: 14″ to 20″ blade
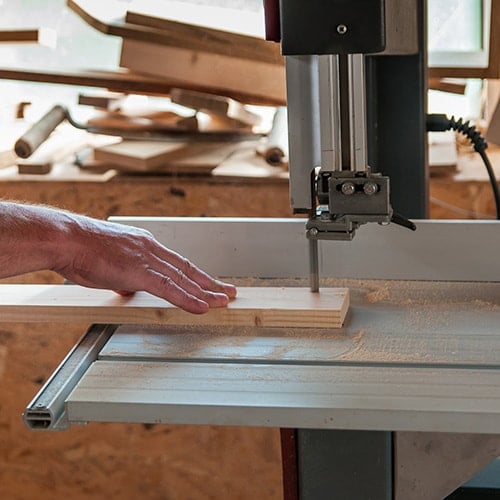

5. Band Saw
Band saws are known for their precision and safety, permitting operators to complete cutting tasks without risking kickback. The saw consists of a continuous loop of sharp, fine teeth made from steel or carbide, known as a band, mounted on two or more wheels. These wheels rotate, allowing the band to move continuously. Most band saws have a heavy table as a base, making them stationary, but there are a few portable and handheld options available.
- Type: Stationary power saw
- Best for: Low-depth vertical cuts
- Average size: 14″ between the column and blade
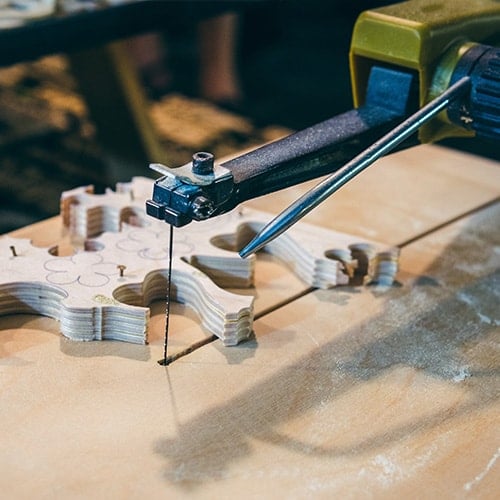
6. Scroll Saw
Commonly used in woodworking, a scroll saw creates intricate, patterned cuts into wood. Its narrow blade continuously oscillates in the center of the saw while the operator manipulates the material to get the desired pattern. The result can range from precise, rounded curves to intricate designs, allowing woodworkers to showcase their artistry.
- Type: Portable power saw
- Best for: Precise patterned cuts
- Average size: 10″ to 30″ throat depth
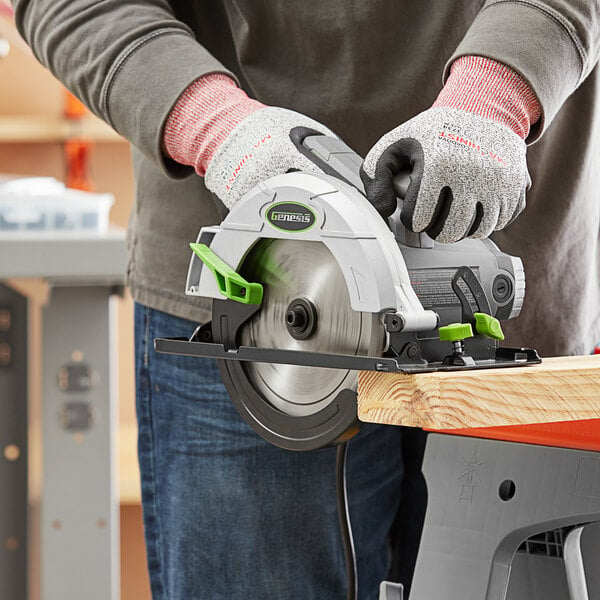

7. Circular Saw
As one of the most well-known power saws, a circular saw’s portability and versatility allow operators to use it for many tasks. With a large, circular blade and lightweight frame, this handheld saw can cut through wood, metal, stone, or plastic. However, inexperienced operators might struggle to control a circular saw due to the blade motion, so keep a firm grip on the handle when using it.
- Type: Handheld power saw
- Best for: Portability, versatility, precise straight cuts
- Average size: 4.5″ to 7.25″ blade diameter
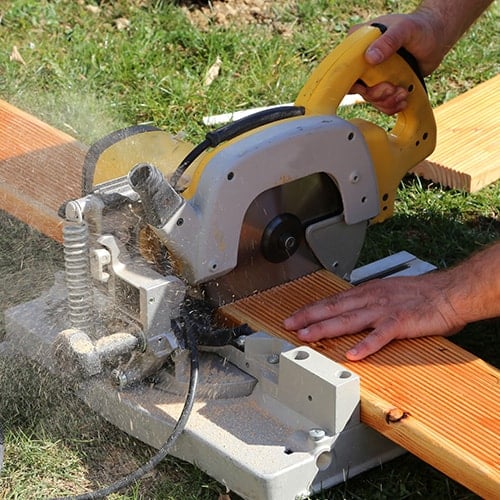

8. Chop Saw
A chop saw is similar to a miter saw, but it has a larger, toothless blade and only makes vertical crosscuts. The blade style allows operators to cut hard materials like metal or stone without damaging the saw. Moreover, chop saws have a portable design that’s easy to pack away and transport between job sites. Position the material on the saw surface and lower the blade using the lever to make the cut.
- Type: Portable power saw
- Best for: Repeated vertical cuts of tough materials
- Average size: 14″ to 15″ blade
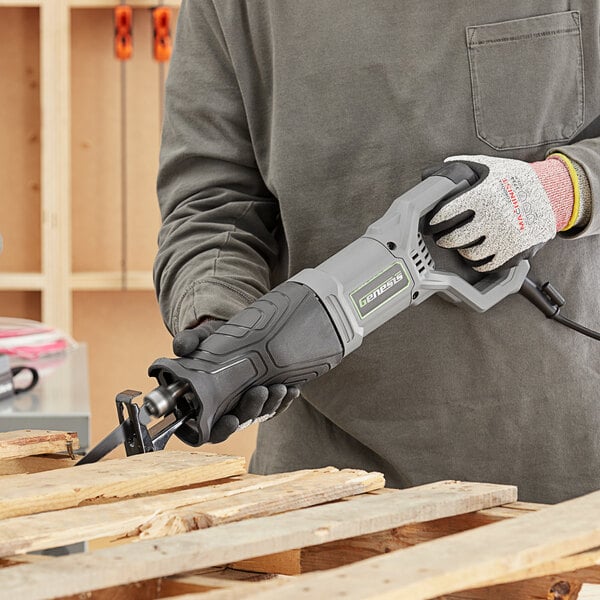

9. Reciprocating Saw
A reciprocating saw features a long, straight blade that protrudes from the front of the tool’s body and moves back and forth in a reciprocating motion. This movement allows quick and efficient cutting through different materials such as wood, metal, or plastic. Since the saw is not known for precision, operators use it primarily on construction sites for demolition.
- Type: Handheld power saw
- Best for: Demolition, portability
- Average size: 3″ to 12″ blade length
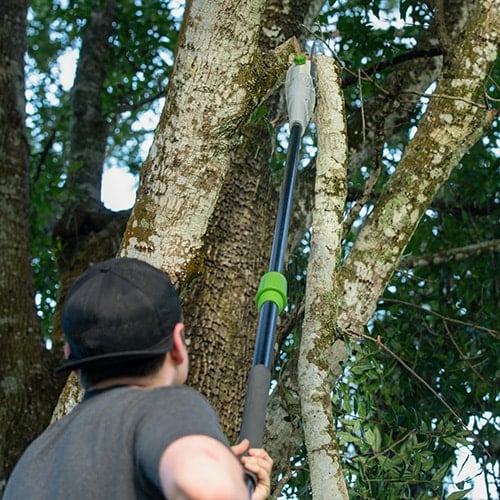

10. Pole Saw
A pole saw is a small chainsaw or saw blade mounted on top of a long pole, allowing operators to reach tall heights from the safety of the ground. The blade can cut small branches, sticks, and leaves to trim trees and shrubs easily. While most pole saws are powered by gas or electricity, some operators prefer manual options for landscaping.
- Type: Portable power saw, manual options available
- Best for: Trimming tall trees and hedges, landscaping
- Average size: 8 to 12 ft. pole for medium, 15 to 20 ft. pole for large
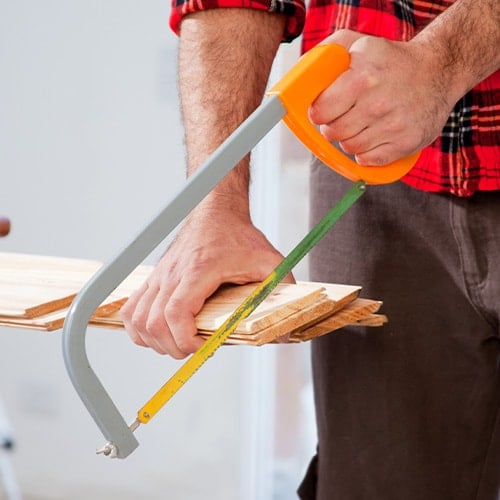

11. Hack Saw
Hack saws typically consist of a C-shaped frame with a handle at one end and a replaceable blade, usually high-carbon steel, at the other. Operators typically use it to cut through metal or plastic. Use caution when cutting wood to ensure you don’t damage the thin blade. When using a hack saw, move the tool in long, steady strokes and avoid excessive force for the best results.
- Type: Handheld manual saw
- Best for: Crosscutting metal or plastic pipes, rods, or dowels
- Average size: 12″ blade length
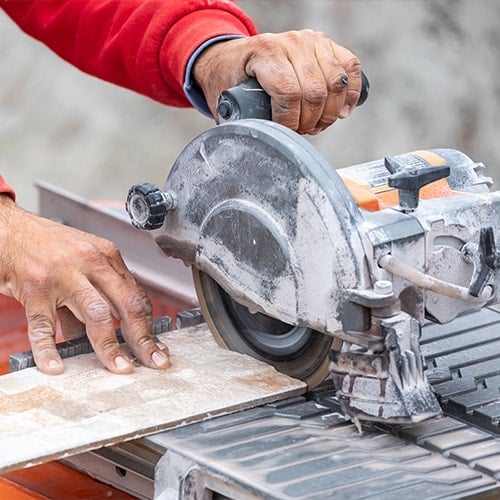

12. Tile Saw
A tile saw typically consists of a flat table or platform with a circular, diamond-coated blade that extends from the bottom. Thanks to the adjustable blade, operators can set the desired cut depth for specific projects. Many models also have a water reservoir or pump system to keep the blade cool and minimize dust during use.
- Type: Portable power saw
- Best for: Cutting ceramic, porcelain, or stone tiles and flooring
- Average size: 7″ to 10″ blade diameter
Saw Safety
Working with saws poses risks to any operator, no matter their experience level. Handheld power saws can be difficult to control, and stationary power saws require constant attention while running. To mitigate the potential for workplace injuries, follow these safety instructions when using a saw.
- When operating a stationary saw, use a push stick or block to maintain a safe distance from the blade.
- Maintain a firm, two-handed grip on handheld saws during use.
- Always keep your hands out of the blade’s path and avoid wearing loose clothing that may get caught in the saw.
- Before operating a power saw, ensure the blade guard and anti-kickback pawls are properly installed.
- Wear appropriate personal protective equipment, such as safety goggles and hearing protection, to safeguard against flying debris and excessive noise.
- Never climb a ladder with a saw, even one switched off.
- Keep the area around a saw and the operator clear while the saw is in use. Before turning a saw on, check the vicinity for hazards and clear them.

